
Shyam S. Mohapatra
University of South Florida, USA
Title: Anti-fusion targeted nanomicellar theranostics: Novel antiviral strategies for respiratory syncytial virus infection-induced lung diseases.
Biography
Biography: Shyam S. Mohapatra
Abstract
The respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), is an important pathogen that infects an estimated 64 million people and causes ~200, 000 deaths globally every year. Despite progress in the biology of RSV, there is no effective treatment or vaccine against RSV infection. Currently, only high-risk infants receive antibody-based prophylaxis, which is expensive and moderately effective in reducing hospitalization. Therefore, a broadly applicable, effective and inexpensive approach to prevent or treat RSV-bronchiolitis or -pneumonia remains an urgent unmet need. We have been investigating nanomedical approaches against RSV infection and have reported on a variety of different strategies including genome vaccine, and siRNA based nanoparticles. More recently, we have developed a novel prophylaxis and/or therapy against RSV infection was inspired by the following discoveries. i) A platform of phospholipid micellar nanoparticles (PMN) was developed, which when given intranasally delivers payload predominantly to the lung. ii) A decoy short heptad repeat (HR)2 peptide was identified, which effectively inhibits the RSV-cell fusion. iii) Human mesenchymal cells were found to be highly susceptible to RSV. The latter aided in establishing a novel 3D scaffold for anti-RSV drug screens, which consisted of creating a completely naked mouse lung scaffold(nMLS) by completely decellularization and recellularizing the nMLS with desired human cells such as including hMSCs and epithelial cells and then infecting the cells in scaffold with RSV with or without drugs. iv)
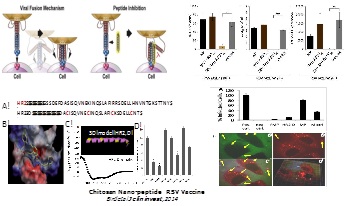
A robust immunocompromised mouse model was created by combining cyclophosphamide treatment with infection by a highly mucogenic strain, RSV-L19F. These developments have led to the hypothesis that a RSV-targeted PMN (RTPMN), combining HR2D anti-fusion peptide, and plasmid encoded siRNAs against RSV-NS1 can provide a safe, effective and inexpensive anti-RSV prophylaxis and/or therapy. The completion of preclinical formulation of anti-RSV PMN-based prophylactics and therapeutics is expected to pave the way to IND-driven studies and clinical trials.

